History: 65 year old male with a history of chronic lymphocytic leukemia presents with left sided chest pain, shortness of breath, and hypoxia after a CT-guided biopsy of a left lung mass.
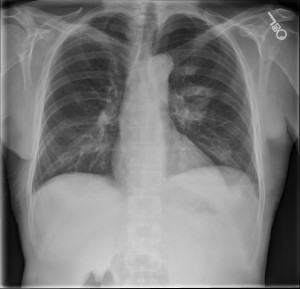
This is an iatrogenic pneumothorax in a patient status post lung biopsy. This patient had a cavitary lung mass.




Leave a comment